There is only thetauvc.c
libuvc-theta-sample/gst/thetauvc.c at master · ricohapi/libuvc-theta-sample · GitHub
BTW, I was able to compile OpenCV 4.4 on the Nano and use OpenCV with Python accessing the theta on /dev/video0. I’m not familiar with gstreamer and this may not be what you want.
I was also able to use gst-launch from the command line with /dev/video0.
I read this blog and the technique the author used for Python was with gstreamer and opencv.
This video has some information on my initial test
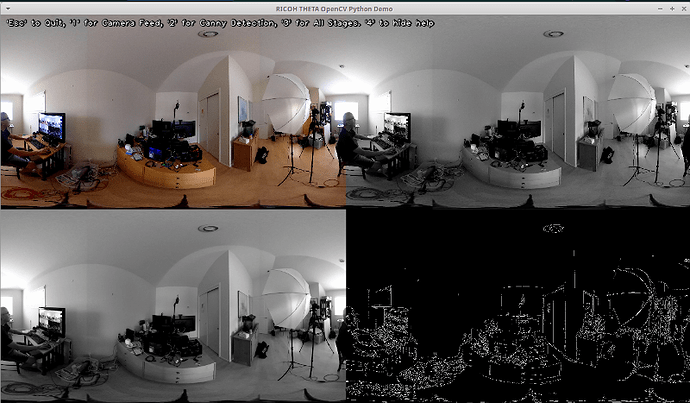
I’ve since improved the OpenCV Python script performance with the recompile.
The test pipeline is:
$ gst-launch-1.0 -v v4l2src ! videoconvert ! videoscale ! video/x-raw,width=1000,height=500 ! xvimagesink
This is with gst-loopback running.
Also, cuda does appear to be working with OpenCV. I have not run these tests yet, but this looks quite useful.
Now with Canny edge detection in real-time. Code sent to meetup registrants.
Update: Aug 29
I’m having some problems with the nvidia-inference demos streaming from the THETA.
Normal webcam works. I’m trying to reduce the THETA 4k output to 2k, but can’t figure how to do this. The camera does support streaming at 2k, but I’m not sure how to force it to use the 2k stream for initial testing
Update Aug 29 night
I can now get a 2K stream to /dev/video0
$ v4l2-ctl --list-formats-ext
ioctl: VIDIOC_ENUM_FMT
Index : 0
Type : Video Capture
Pixel Format: 'YU12'
Name : Planar YUV 4:2:0
Size: Discrete 1920x960
Interval: Discrete 0.033s (30.000 fps)
$ v4l2-ctl --list-devices
Dummy video device (0x0000) (platform:v4l2loopback-000):
/dev/video0
Update Aug 30 morning
I have /dev/video0 working smoothly on x86 with v4l2loopback thanks to @Yu_You submission on GitHub. I added this and the following info to the meetup early access documentation:
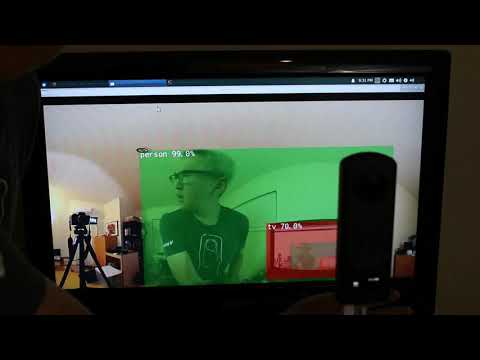
- video demo and code for DetectNet running on Nvidia Jetson Nano with Z1 using live stream. Good object detection of moving person in real-time
- video demo and code for Canny edge detection with Python cv2 module. In real-time with minimal lag
- explanation and code snippet to change video resolution from 4K to 2K for testing on Nano
Link to sign up for the meetup is at the Linux Streaming Site. Once you register for the meetup, you’ll see a page immediately with a link to early-access documentation and code. We’re not trying to sell you anything. We’re gating the content so that we can show results to our sponsor, RICOH. This helps us to secure sponsor budget to continue working with the community and produce informal documentation. If you miss the meetup, we’ll put the documentation up on the site in a week or two.
DetectNet running at 23fps. Accurate identification of person and TV.
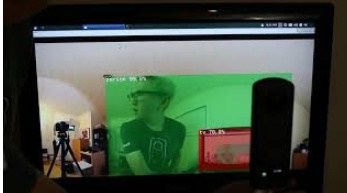
Update Sept 4 - morning
video demo of DetectNet
x86 test using guvcview
Update Sept 4, 2020
Current plan in order of priority
- publish meetup-specific documentation and technical QA to people that registered for documentation. Likely next week.
- retest gphoto2 on x86 or Nano (Ubuntu) with THETA USB API based on this discussion, Test gp Python module for easier access of THETA USB API from inside of Python programs
- install separate SSD on x86 and retest gstreamer and graphics system with hardware acceleration and resolution at 4K and 2K
- if successful, install ROS on x86